
- Phone: (123) 0200 12345
- Mailus@TheExperts.com
- Stay Connected:
2023 June

Inter-American Development Bank Quarterly Business Review: First Quarter 2023
Year: 2023
The 2023 first quarter edition of the Quarterly Business Review (QBR) provides management with a status of the Bank's performance. The QBR reports on outputs, lending program priorities and organizational indicators on a quarterly basis to allow management to monitor progress in achieving corporate results. This periodic monitoring supports evidence-based decision making and allows for timely identification of deviations from targets and enables effective implementation of measures to address them.
Author: Inter American Development Bank
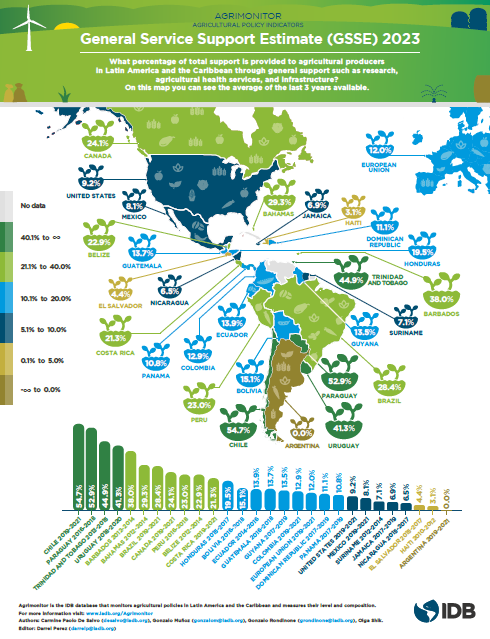
Agrimonitor Agricultural Policy Indicators: General Service Support Estimate (GSSE) 2023
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Agriculture / Farming, Health, Infrastructures, Policy / Governance, Public Sector, Publications, Sustainability | 0 Comment
This infographic illustrates the level of support provided to the agricultural sector as a whole through services such as research, development, training, inspection, marketing, and promotion. The indicator used is the General Service Support Estimate (GSSE), which is expressed as a percentage of the Total Support Estimate (TSE).
Author: De Salvo, Carmine Paolo; Muñoz, Gonzalo; Rondinone, Gonzalo; Shik, Olga

Estimating and mapping natural hazards and risk reduction provided by coastal ecosystems
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Biodiversity Protection, Climate / Resilience, Environment / Ecosystem, Publications, Risk | 0 Comment
This report presents two case studies in which coastal vulnerability modeling was used to quantify the role those coastal ecosystems play in reducing risk to coastal communities now and with future sea-level rise. These analyses were used to inform post-disaster reconstruction and coastal resilience building efforts as well as climate change adaptation strategies.
Author: Arkema, Katie; Bailey, Allison; Chávez Cerón, Valeria; Guerrero Compeán, Roberto; Menéndez Fernandez, Pelayo; Reguero, Borja; Ruckelshaus, Mary; Silver, Jessica

Tax Transparency in Africa 2023: Africa Initiative Progress Report
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Developing countries, Economic Development / Stability, Policy / Governance, Public Sector, Publications, Transition & Transparency | 0 Comment
The Africa Initiative has developed and expanded its capacitybuilding activities to ensure transparency and exchange of information (EOI) benefit African countries. In 2022, five African countries reported identifying EUR 76.6 million of additional revenues (tax, interests and penalties) through EOI, the highest amount since the launch of the Africa Initiative in 2014.
Author: African Union, OECD & ATAFTAX

Inherited inequalities: intergenerational mobility in Latin America and the Caribbean
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Development, Economy, Human Development, Human Resources, Publications | 0 Comment
Latin America and the Caribbean is one of the most unequal regions in the world. Not only is this inequality high, but it is even excessive for the level of development of the region, indicating a kind of Latin American exceptionalism. Moreover, inequality in the region is not new, with its origins dating back to colonial times. Despite the many advances achieved in different economic and social development indicators in recent decades, average inequality levels in the region have not changed substantially or sustainably. Beyond countryspecific nuances, they continue to be a characteristic feature of Latin American and Caribbean societies. The Report on Economic Development 2022 (RED 2022) states that the high inequality in the region has very deep roots, driving its persistence over time. As a result of this inertia, who the most and least wealthy or advantaged individuals and families are has persisted steadily over time. RED 2022 documents and explains the evolution of intergenerational mobility in the region, assessing the multiple dimensions that determine the levels of wellbeing of parents and children.
Author: CAF

Wealth Inequality in Latin America
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Economic Development / Stability, Economy, Human Development, Policy / Governance, Public Sector, Publications | 0 Comment
How much wealth has accumulated in the region and how is it distributed across households? Despite being widely recognized for its extreme income inequality, reliable data on wealth is scarce, partial and oftentimes contradictory, making it difficult to answer these basic questions. In this study, we estimate aggregates based on macroeconomic data, and inequality based on recently available surveys. We contrast our results with the literature, with a handful of state-of-the-art estimates from administrative sources, and with more available but extrapolated estimates from Credit Suisse and wid.world. Considering all the evidence, we distinguish reliable facts from what can only be conjectured or speculated. We find that aggregate wealth increased over two decades in four countries, now ranging close to 3.5 the national income for market value estimates and 5-6 times at book values. We also find that wealth inequality is amongst the highest in the world were it can be measured. Given data limitations, one can only speculate about aggregates in opaque countries and about inequality trends in any country in the region.
Author: Carranza, Rafael; De Rosa, Mauricio; Flores, Ignacio

Access to Credit and the Expansion of Broadband Internet in Peru
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Banks, Finance, Infrastructures, Publications, Technologies & Innovations | 0 Comment
We exploit the staggered expansion of the internet broadband network to firms and bank branches locations in Peru during the last decade to study non-financial firm performance and bank credit dynamics. Access to broadband unleashes firm growth, increases the chances of entry of firms and reduces the probability of exit in benefited locations. For those firms that had a borrowing relation with a bank before the expansion of broadband, the increase in sales serves as a signal to banks about their profitability, which in turn respond by providing more credit. Entry and exit from
the credit market follows a similar pattern as in the case of firms, but the results take longer to materialize after the shock. We can disentangle supply and demand effects, since there is a group of firms and bank branches with different locations and asymmetrical timing for the availability of the technology. Our analysis highlights the importance of the demand channel in the reduction of the observed interest rates, which is consistent with the fact that our credit market results are concentrated among micro and small firms
Author: Cusato, Antonio; Castillo, José Luis; IDB Invest

Taxation of the Mining Industry in Latin America and the Caribbean: Analysis and Policy
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Environment / Ecosystem, Policy / Governance, Public Sector, Publications, SDGs | 0 Comment
Little is known about mining taxation in Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), although it is both particularly complex and has large effects on incentives for investments in mining activities. This paper reviews the types and consequences of mining taxes that are applied in the region and their implications for investment. Most countries assess royalties based on the value of production, which are consistent with royalties applied globally. However, miners confront additional taxes such that tax regimes, in the aggregate, inefficiently discourage investment, including income taxes, non-refundable sales taxes on capital purchases, capital taxes, gross receipt taxes, and real estate transfer taxes. Several reforms emerge from the analysis. The most important is for LAC countries to consider profit-based regimes--similar to Chile, Mexico, and Peru--supplemented by a minimum royalty based on the value of production. Company tax reforms should also be considered with the aim to tax mining similarly to other sectors of the economy to improve the allocation of capital.
Author: Bazel, Philip; Mintz, Jack M.; Reyes-Tagle, Gerardo

OVERVIEW OF AFRICA’S FINANCIAL SECTOR Long term finance and capital markets1
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Banks, Finance, Market, Policy / Governance, Public banks, Publications | 0 Comment
Expanding on the general overview of the financial sector in Africa, this second article focuses on the development of the capital markets and the recent initiatives to attract long-term capital to the continent. Capital markets in Africa are still in their infancy and mirror the economic development of the continent. However, the evolution over the last decade prior to COVID-19 pandemic underscores the growth potential. The number of stock exchanges have grown from seven in the 1980s to 30 in 2020. The evolution of financial markets mirrors the economic development of the region. The market capitalisation of the JSE (Johannesburg Stock Exchange ) alone accounts for more than 80% of the entire ASMs, while the rest of the stock exchanges are characterized by low market capitalisation, few domestic companies, small size of listed firms and low levels of liquidity with few shares mostly dominating total trading activity. The biggest ones are at a very advanced stage of interconnection that has increased liquidity and product diversification. The article profiles the ongoing efforts towards improving the available long-term financial resources with institutional investors.
Author: Albert A. Agyemang-Badu; Muazy Ibrahim; Fernando Gallardo Olmedo; Guy Roger Menan; Juan Antonio Obregón; Hugues Kamewe Tsafack

Public banks, public water: exploring the links in Europe
Year: 2023
by Kevin Fiestas | Climate / Resilience, Finance, Infrastructures, Public banks, Publications, Water & Sanitation | 0 Comment
Public banks have played an important role in financing public water
and sanitation services in Europe for over a century, but these activities
have been largely ignored in the academic literature. This special issue
is an initial corrective to this research gap, providing conceptual
insights and empirical information on eight countries and regions in
Europe, covering a wide range of public banks working with public
water operators. This introductory article provides background rationale
for the research, outlines our methodologies, frames the theoretical
potentials of public banks in the water sector, highlights key
findings and points to future possible research directions.
Our main conclusion is that public banks have an important role to play in funding
sustainable and equitable WSS in the European region, but that there is considerable
scope for expansion and significant room for improvement. We begin this introduction
with a summary of our theoretical understanding of what constitutes a ‘public bank’, to
situate where we stand on the topic and to introduce Water International readers to what
may be an unfamiliar subject matter.
Author: Marois, Thomas & McDonald, David A.
- Demographic Observatory Latin America and the Caribbean 2023. Population dynamics in Latin America and their effects on the labour force
- Implications of Current Cocoa Price Hikes on African Trade and Macroeconomic Performance
- Report of the 2023 AADFI-ADFIAP Joint International CEO Forum
- 2024 Latin American and Caribbean Macroeconomic Report: Ready for Take-Off? Building on Macroeconomic Stability for Growth
- Africa In Figures 2023